Font Size
- S
- M
- L
Business Consulting
TSE disclosure documents/support for official gazette notices

The Tokyo Stock Exchange (TSE) is one of the world’s largest financial markets, playing a critical role in maintaining transparency and trust in corporate activities. Disclosure documents submitted to this exchange serve as essential tools for investors, regulators, and analysts to assess the financial health and operational integrity of listed companies. This article explores the various aspects of these filings, including their purpose, current trends, technological innovations, and new developments.
What Are Tokyo Stock Exchange Disclosure Documents?
Purpose and Overview
Disclosure documents are legal and financial filings required by the TSE to ensure transparency among listed companies. These filings typically include financial statements, quarterly reports, corporate governance details, and material information about business operations. They serve to protect investors by providing a clear and accurate picture of the company’s activities, strategies, and risks.
Key Types of Disclosures
– Financial Statements: These include income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow reports, providing a snapshot of a company’s financial health.
– Timely Disclosure: Companies are obligated to report material changes, such as mergers, acquisitions, or significant market developments, as soon as they occur.
– Corporate Governance Reports: These outline the internal systems and policies ensuring responsible management.
Significance for Stakeholders
Investors use these filings to make informed decisions, while regulators rely on them to enforce compliance. For companies, accurate and comprehensive disclosures help build market confidence and attract long-term shareholders.
Current and Future Trends in Disclosure Practices
Increased Focus on ESG Reporting
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria have become a focal point in financial markets worldwide. TSE has encouraged companies to include ESG-related data in their disclosures. This trend aligns with global investor demands for sustainable and socially responsible investment opportunities.
Standardization and Global Alignment
To facilitate cross-border investment, efforts to harmonize disclosure standards with international frameworks such as the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) are gaining momentum. Many companies are adopting these standards to appeal to global investors.
Digital Transformation of Reporting
The transition from paper-based to digital reporting formats has streamlined access to disclosure documents. The TSE provides a centralized online platform where investors and analysts can easily retrieve and analyze these filings, enhancing transparency and accessibility.
Technological Innovations Impacting Disclosure Practices
The Role of XBRL in Financial Reporting
The Extensible Business Reporting Language (XBRL) has revolutionized how financial data is structured and shared. By enabling automated data extraction and analysis, XBRL improves the efficiency and accuracy of financial reporting, benefiting both companies and investors.
AI and Data Analytics in Document Analysis
Advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning are transforming the way disclosure documents are analyzed. These tools can quickly identify patterns, anomalies, or risks within vast amounts of data, enabling investors to make faster and more informed decisions.
New Developments and International Perspectives

Revised Corporate Governance Code
The TSE recently updated its Corporate Governance Code, emphasizing greater transparency and shareholder engagement. Companies are now expected to disclose more detailed information on board diversity, executive compensation, and risk management practices.
Regional Variations in Disclosure Requirements
While Japan’s disclosure framework is robust, there are differences compared to other major markets like the U.S. or Europe. For instance, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act in the U.S. imposes stringent internal controls, while European regulations often emphasize sustainability reporting. Understanding these nuances is crucial for multinational companies operating in Japan.
Expansion of Global Investment
With Japan attracting increased attention from foreign investors, the demand for English-language disclosure documents has risen. The TSE has responded by promoting the adoption of bilingual reporting, making it easier for global stakeholders to access critical information.
Staying Ahead in a Changing Disclosure Landscape
The landscape of disclosure practices on the Tokyo Stock Exchange continues to evolve, shaped by technological advancements, regulatory updates, and shifting investor priorities. Companies must adapt by embracing digital tools, aligning with global standards, and prioritizing transparency. For stakeholders, understanding these developments is essential to navigating Japan’s dynamic financial markets effectively.
What Are Official Gazette Announcements?

The Official Gazette of the Japanese Government, or “Kanpō,” serves as a critical channel for disseminating legal, administrative, and regulatory information. As an official publication, it provides the public with transparency regarding government activities, ensuring that individuals, organizations, and businesses are well-informed. This article addresses the key aspects of these announcements, exploring their significance, current trends, technological advancements, and international perspectives.
Purpose and Function
The Official Gazette acts as the Japanese Government’s formal platform for announcing new laws, amendments, public notices, and decisions. Its primary purpose is to ensure that citizens and businesses can access authoritative information regarding regulations, policies, and official procedures.
Key Components of the Gazette
Announcements published in the Gazette include:
– Legal Notices: Information on enacted or revised laws and ordinances.
– Administrative Notices: Updates on regulatory frameworks and policy changes.
– Judicial Announcements: Public notices regarding court decisions or bankruptcy proceedings.
– Business and Individual Notices: Including patents, trademarks, and official name changes.
Historical Significance
The Gazette was first published in 1883, reflecting the modernization of Japan’s administrative system during the Meiji Era. It remains a cornerstone of governmental transparency, adapting over time to meet the needs of a digitally connected society.
Current and Future Trends in Gazette Publications
Digital Transformation and Accessibility
With the growing emphasis on digitalization, the Official Gazette is now available online, making it more accessible to a broader audience. Citizens and businesses can search announcements through an electronic database, streamlining access to vital information.
Global Comparisons
Japan’s approach mirrors global trends, where official publications in countries like the United States (Federal Register) and the United Kingdom (London Gazette) have similarly adopted digital platforms. These changes cater to the modern demand for real-time information while maintaining accuracy and reliability.
Transparency in Government Activities
The publication of timely and detailed announcements reflects the Japanese Government’s commitment to transparency. Recent efforts to include more user-friendly summaries and categorized indexes have further improved usability.
Technological Innovations in Gazette Management
AI for Information Categorization
Artificial intelligence is increasingly used to categorize and tag content in the Gazette. These systems enable more precise keyword searches, helping users navigate complex legal and administrative documents efficiently.
Enhanced Digital Platforms
The Gazette’s digital platform now offers multi-language support, catering to international businesses and expatriates in Japan. Furthermore, subscription services allow users to receive notifications tailored to their specific interests, such as legal changes or intellectual property updates.
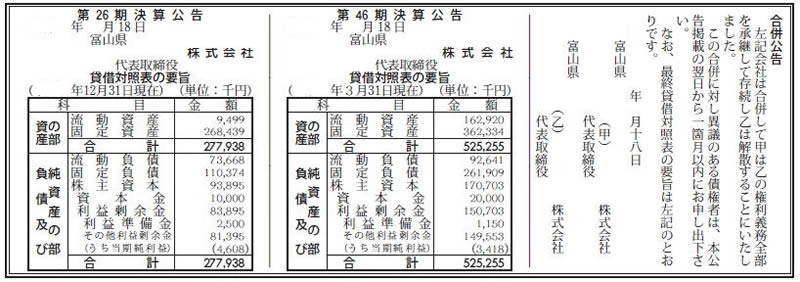
International and Regional Perspectives on Government Announcements
Cross-Border Relevance of Gazette Notices
In an interconnected world, the Gazette’s announcements often have international implications. For instance, foreign businesses investing in Japan monitor these notices to stay updated on tax reforms, trade policies, and compliance requirements.
Regional Developments in Asia
Countries in Asia, such as South Korea and China, also publish their own official gazettes. Comparing these systems highlights variations in transparency, accessibility, and technological adoption. Japan’s focus on digitization positions it as a leader in delivering official information efficiently.
Impact on Local Governance
Regional governments within Japan often supplement national announcements with localized information. These notices help align municipal regulations with overarching policies, ensuring consistency and clarity for residents and businesses.
New Developments in Gazette Content and Distribution
Expansion of ESG-Related Notices
The increasing importance of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria has led to a rise in related announcements, including policies on sustainability and corporate accountability. Businesses closely follow these updates to align with regulatory expectations.
Simplification of Complex Language
In response to public feedback, efforts are underway to simplify the technical language often used in announcements. These changes aim to make legal and administrative updates more accessible to non-specialists.
Integration with AI-Powered Legal Tools
Legal professionals can now integrate the Gazette with AI-powered platforms to automatically track and analyze updates relevant to their fields. This functionality reduces the burden of manual monitoring while ensuring comprehensive compliance.
Staying Informed in a Changing Landscape
The Official Gazette of the Japanese Government remains an indispensable resource for individuals, businesses, and organizations. As it evolves through digital innovations and user-focused improvements, its role in promoting transparency and accessibility becomes increasingly vital. By understanding and utilizing this resource effectively, stakeholders can stay informed and prepared in an ever-changing regulatory environment.






